Warehouse distribution is the unsung hero of the eCommerce and direct-to-consumer (DTC) industries, ensuring the smooth transit of goods from manufacturers to consumers. With eCommerce revenues in the US expected to increase 15.4% to over $900 in 2023, companies of all sizes must invest in this key component of their distribution network.
In this article, we’ll explore fulfillment centers and how they work, the differences between a warehouse and a distribution center, and the major trends impacting how companies approach warehouse distribution to meet evolving customer expectations around delivery.
With that said, let’s dive into the world of warehouse distribution and how it’s changing in the digital era.
Understanding Warehouse Distribution
The word “warehouse” brings to mind large commercial buildings filled with shelves and skids of products. But warehouses are more than just storage facilities; they’re pivotal hubs where inventory management, order processing, and logistics come together to drive successful fulfillment operations.
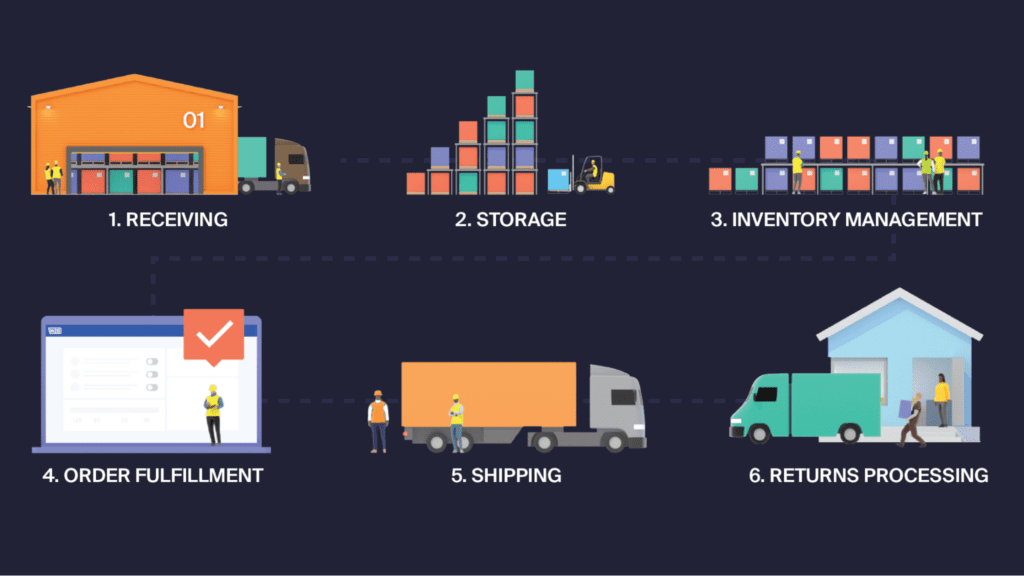
Here’s a quick overview of the key supply chain operations that occur through warehousing:
- Receiving Goods: Warehouses receive products from manufacturers or suppliers. This stage involves checking the quality and quantity of goods, confirming accuracy against an advanced shipment notice (ASN), and then storing them appropriately.
- Storage: Goods are stored until they’re needed. This involves organizing products in a way that maximizes space and efficiency, like slotting or warehousing. It may also include specialized storage for certain types of products (e.g., refrigeration for perishable goods).
- Inventory Management: Keeping track of inventory levels to ensure there’s enough product to meet demand without overstocking can lead to increased storage costs or low stock. This is especially important considering the changing requirements of companies like Amazon.
- Order Fulfillment: When an order is received, the storage costs or stockouts duct is retrieved from the warehouse, packaged, and prepared for shipment. Depending on the scale of operations, this eCommerce fulfillment process can be manual or automated.
- Shipping: The final step involves sending the products to their destination, whether it’s a retail store, another warehouse, or directly to the consumer.
- Returns Processing: This requires handling returns and exchanges, which involves inspecting returned goods and deciding whether to restock them, dispose of them, or send them back to the manufacturer.
In the pre-digital retail model, businesses would store products in a warehouse before sending them to retail stores or wholesalers. Now, these same businesses need to adopt omni- or multichannel models where they sell to customers through marketplaces like Amazon and eCommerce platforms like Shopify. Incorporating this growing number of online vendor options to reach new customers adds another layer of complexity to the supply chain.
As eCommerce continues to grow, the role of warehouse distribution is on the rise and comes with an array of benefits, including decreasing time in transit, enabling faster shipping without increasing operating costs, and more.
Differentiating Warehouses and Distribution Centers
Increasingly, the term warehouse is swapped out with phrases like “fulfillment center.” This leads to an important question: What’s the difference between a warehouse and a distribution center?
The rise of major online retailers like Amazon and Walmart has given smaller businesses insight into the efficiencies of using third-party logistics, technology, and warehouse networks.
Warehouses are primarily used to store goods for longer periods. They’re essential for businesses that must stockpile inventory, especially those dealing with seasonal fluctuations or bulk purchases.
Distribution Centers, on the other hand, are more dynamic and designed for the rapid movement of goods using a hub and spoke model. They cater to the immediate processing of inbound and outbound shipments, making them critical for eCommerce businesses prioritizing speed and efficiency in order fulfillment.
The impact these core supply chain components can have can vary depending on the following characteristics:
- Size: Distribution centers are typically larger than traditional warehouses due to their need to accommodate a greater volume of goods and more complex handling equipment.
- Location: Strategic location is crucial — especially now that customers expect same-day or next-day delivery. Ideal regional distribution centers are situated near major transport hubs, highways, and urban centers to facilitate quick distribution.
- Customers: Fulfillment centers often cater to specific eCommerce and DTC businesses, necessitating a more tailored approach to inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Technology: Advanced technology is a hallmark of modern distribution centers. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), cutting-edge Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and sophisticated sortation systems are commonly employed to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
But online retail isn’t all fun and games. There are some significant challenges that operations lead and supply chain managers face when it comes to warehouse distribution.
6 Top Warehouse Management Challenges
Let’s take a look at the six largest challenges impacting warehouse management:
Reducing Long-Zone Shipping
Long-zone shipping involves delivering goods over extensive distances, which can be costly and time-consuming. Businesses struggle to find cost-effective strategies to minimize these expenses while maintaining timely deliveries. Effective solutions optimize transportation routes, leverage strategic warehouse locations, and deploy advanced logistics technologies to streamline these processes — all for the ultimate goal of reducing time in transit (TNT).
Costly Insourced Fulfillment
Managing in-house fulfillment operations means a sizable investment in infrastructure, technology, and labor. Companies often face high overhead costs, challenges in scaling operations, and difficulties in adapting to fluctuating market demands. Outsourcing to specialized logistics providers offers a more scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient solution.
Labor and Space Restraints
Adequate staffing and space allocation are critical for efficient warehouse operations. Companies frequently encounter challenges in hiring skilled staff and expanding physical space to meet growing business needs. This limitation can lead to bottlenecks in fulfillment processes, impacting overall operational efficiency and customer service levels.
Lack of Control or Visibility into the Warehouse
Without real-time visibility and control over warehouse operations, businesses face challenges in tracking inventory, managing resources, and responding to market changes promptly. Implementing integrated management systems and adopting technologies can enhance visibility, control, and responsiveness in warehousing operations.
Warehouse Issues
Common issues like inventory discrepancies, shipping inaccuracies, and fulfillment delays stem from inadequate physical operations and outdated warehouse management systems. These problems lead to customer dissatisfaction and potential revenue loss. Addressing these requires robust inventory management, intelligent order orchestration, and responsive customer service mechanisms.
Customer Dissatisfaction Due to Slow Delivery
Online shoppers expect quick delivery times. In fact, 72% of consumers actually opt for premium same-day delivery services mainly due to urgency.
Delays in shipping can result in customer dissatisfaction and harm brand reputation. Businesses need to streamline their fulfillment processes and leverage efficient distribution networks to ensure timely delivery and maintain customer satisfaction.
With these challenges in mind, take a look at the trends shaping how eCommerce and DTC leaders approach warehouse distribution.
3 Trends Shaping the Future of Warehouse Distribution
The landscape of warehousing is rapidly evolving, driven by the ever-changing demands of eCommerce and direct-to-consumer (DTC) markets. As these industries continue to grow, the warehouses supporting them must adapt and innovate.
Our 2023 Future of Fulfillment Report found three key trends emerging in the online retail space in terms of how companies approach warehouse distribution.
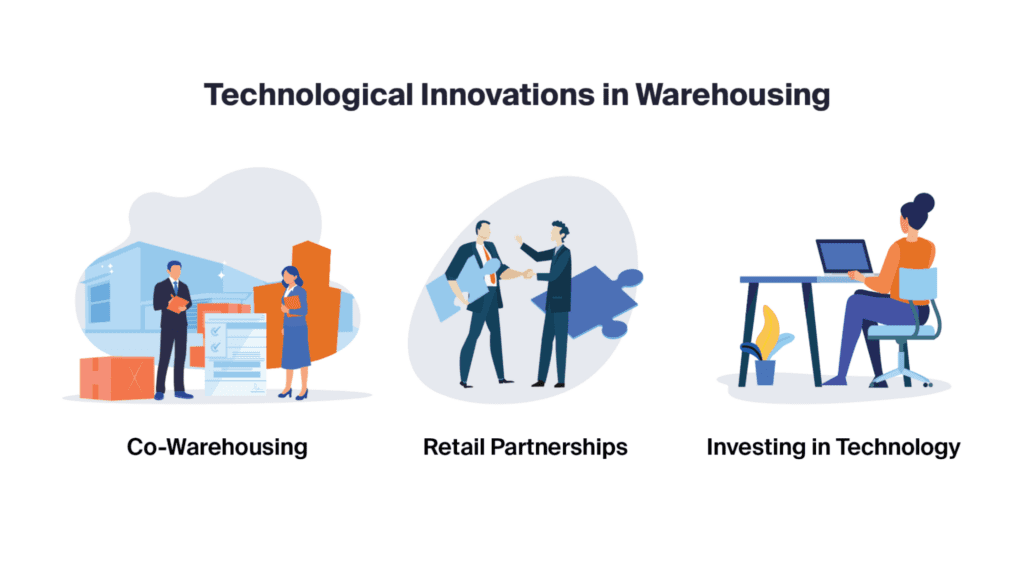
1) Co-Warehousing: A Collaborative Approach
One of the emerging trends in warehouse distribution is the rise of co-warehousing. This concept involves multiple businesses sharing warehouse space and resources and pooling funds to cut expenses.
Over 74% of respondents to our Future of Fulfillment report agree that this practice will be a key part of strategies going forward. That’s because co-warehousing addresses the challenges of high operational costs and space limitations.
The benefits of co-warehousing include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Public warehouses and other shared forms mean shared costs, making warehousing more accessible for smaller businesses.
- Flexibility: Co-warehousing offers scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their space and resource usage based on demand. This can be especially useful for brands with a reliable peak season.
- Collaboration Opportunities: Thanks to cost-sharing, businesses upgrade to more sophisticated, integrated warehouses that they wouldn’t be able to afford to build on their own.
2) Retail Partnerships: Expanding Reach and Efficiency
Another key trend is the formation of retail partnerships. These partnerships allow eCommerce and DTC companies to expand their distribution networks by leveraging the existing infrastructure of established retailers.
Advantages of retail partnerships include:
- Extended Reach: Partnering with retailers can open up new distribution channels and fulfillment networks, drastically increasing the scale of orders handled.
- Improved Customer Experience: Retail partnerships can lead to faster delivery times and better service, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Resource Optimization: Utilizing a retailer’s distribution network can lead to more efficient use of resources and reduced logistics costs.
3) Investing in Technology: The Key to Modern Warehousing
Continued investments in technology are crucial for the future of warehousing and fulfillment. Advanced technologies streamline operations and also provide data-driven insights for better decision-making.
Here are some of the most important technological innovations in warehousing and distribution:
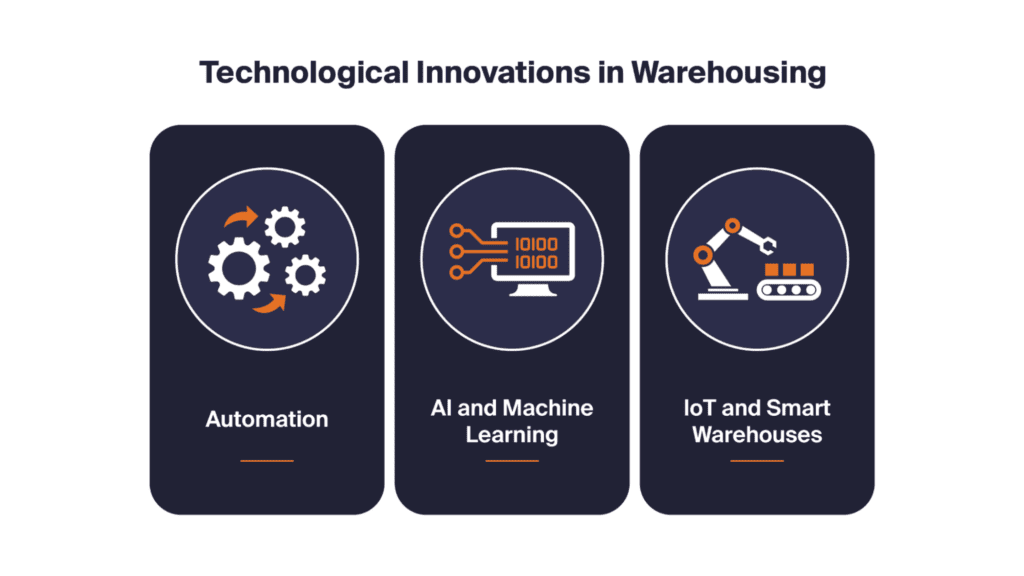
- Automation: From robotic picking systems to automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), technology is reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are enhancing inventory management, demand forecasting, and optimizing logistics operations.
- Smart Warehouses: Smart warehouses are enabling real-time tracking and management of inventory, leading to more transparent and efficient warehouse operations.
Real-World Examples: 2 Success Stories
Optimizing warehouse distribution can have a major impact on the entire supply chain of your business. What easier way to understand this than by looking at the recent successes of other companies in the eCommerce space?
Here are two companies that partnered with Ware2Go to leverage their distribution centers.
Palouse Brand: Embracing Co-Warehousing
Palouse Brand, a fifth-generation farm in Washington State, has successfully scaled its distribution through a strategic partnership with Ware2Go. Initially starting with a modest operation, Palouse’s growth necessitated the adoption of fulfillment partners. Leveraging five of Ware2Go’s 35+ warehouses across the United States enables Palouse to offer consistent one- to two-day shipping to their customers nationwide.
A key aspect of this partnership is Ware2Go’s data-driven approach, which optimizes distribution by analyzing order volumes for each warehouse. Additionally, the integration of Ware2Go’s services with the UPS Network and Coyote logistics ensures reliable transportation and timely delivery. This efficient distribution system is seamlessly integrated with various sales channels, allowing Palouse to focus on its mission of bringing quality food products to homes across the U.S.
The partnership guarantees efficient logistics and also supports Palouse’s vision of being part of people’s mealtime conversations, emphasizing the brand’s commitment to customer connection and satisfaction.
O2: Navigating Market Volatility with Flexible Fulfillment
O2, an innovative recovery drink company, has significantly enhanced its distribution efficiency through a partnership with Ware2Go. Initially challenged by managing multiple fulfillment houses, O2 found a streamlined solution in Ware2Go’s centralized fulfillment services. This partnership has been pivotal, especially when O2 shifted its focus from gym sales to direct-to-consumer channels during mandatory gym shutdowns.
Ware2Go’s adaptability allowed O2 to seamlessly transition and meet new consumer demands. A key aspect of this collaboration is Ware2Go’s integration with O2’s technological stack, including Shopify, facilitating a smooth order and fulfillment process. Ware2Go’s capabilities in handling diverse order sizes — from small individual orders to large gym supplies — further demonstrate their versatility and alignment with O2’s varied customer base.
The partnership has led to significant time and cost savings for O2, allowing them to focus on their core business values. Ware2Go’s scalability and commitment to fast, accurate delivery have been instrumental in O2’s continued growth and ability to meet high customer expectations.
Prepare for the Future of Distribution Today with Ware2Go
The future of warehousing is undeniably intertwined with collaborative strategies, retail partnerships, and technological advancements. For eCommerce and DTC companies, investing in scalable, automated distribution networks that encompass end-to-end tech solutions is not just a trend but a necessity for growth and sustainability in the digital age. Embracing these trends will not only solve current challenges but also pave the way for future success.
Find valuable insights into collaborative warehousing, efficient retail partnerships, and technology—all aimed at enhancing your distribution efficiency.
Get Your Copy of the Future of Fulfillment Report and pave the way for a more profitable, resilient supply chain.